Historians will recount 2025 as a turning point for global health. Paramount was a sizeable drop in global aid funding, precipitated by the U.S. withdrawal from the World Health Organization and the dissolution of the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID). Other countries, including the United Kingdom and various EU members, similarly lowered their financial commitments to global health and multilateral institutions, causing overall health spending to dip to its lowest point in 15 years. Those cuts have disrupted health and food systems in the most vulnerable communities and compound challenges in conflict zones such as Gaza and Ukraine. The true cost of funding cuts, however, will be measured in lives lost—a toll that one end-of-the-year estimate says currently stands around 500,000 to 1,000,000.
Despite that tragedy, bright spots remain. Countries that have traditionally been recipients of foreign assistance—such as Nigeria—have used the moment to build health resilience without donors. Artificial intelligence offered new avenues for diagnostics and surveillance across high-, middle-, and low-income countries, and the World Health Assembly turned long-awaited momentum into the adoption of the Pandemic Agreement.
To cover this year's developments, contributors and journalists spread across six continents published nearly 200 articles with Think Global Health—a selection of which our editorial team has highlighted:
1. President Trump Begins Changing U.S. Global Health Policy
Trump's return to office has raised questions about how America First 2.0 handles global health. Several executive orders in his first week back in the White House began to flesh out what U.S. global health involvement will look like. Some send the U.S. government in definitive directions concerning global health. Others, including the America First directive to the secretary of state, established processes that will shape how the United States engages on global health issues for the next four years.
2. Africa's Quiet Response to U.S. Realignment of Foreign Aid
Characterizing the U.S. withdrawal from foreign assistance as a catalyst for a new era of African strength and self-reliance allows African politicians to emphasize their competence, dignity, and readiness to take on a challenge. The political appeal is undeniable and permits capitalizing on resentments accrued in earlier eras, when the United States used its foreign assistance as leverage to influence a recipient government's decisions. The loss of U.S. influence and leverage is a problem for Washington but could be perceived as liberating from across the Atlantic.
3. China's Failing Bid to Reverse Population Decline
More than three decades later, in response to flagging birth rates, the government reversed itself and loosened population-control efforts. Officials replaced the one-child limit with the universal two-child policy in 2016, then in 2021 upped the maximum number of children per family to three.
These policies did not have the intended results.
4. When Endometriosis Causes Mental Illness
Recently, researchers have called for a comprehensive approach to endometriosis care. A 2024 study suggests health-care providers should view endometriosis as a lifelong condition that requires multiple specialists to work together. This collaborative approach improves patients' quality of life and mental health outcomes.
5. Gain of Fiction: How COVID Origins Motivated Defunding of U.S. Science
It's time to let go of the self-defeating fiction that science, not nature, caused the pandemic and to get serious about the reality that the next serious health or national security crisis could arrive tomorrow. Without science, the United States won't be ready, and the American people—and the world—will pay the price.
6. Bird Flu Roars Back: An Update on Thanksgiving Turkey Prices
Since September 1, an early start for flu season, outbreaks have wiped out nearly 2 million turkeys from farms supplying meat for delis and dinner tables. This toll is five times more than what occurred through mid-November in 2024. Likewise, chicken farms producing consumer eggs have lost 5.7 million hens, on par with the beginning of last year's severe run through egg-laying hens.
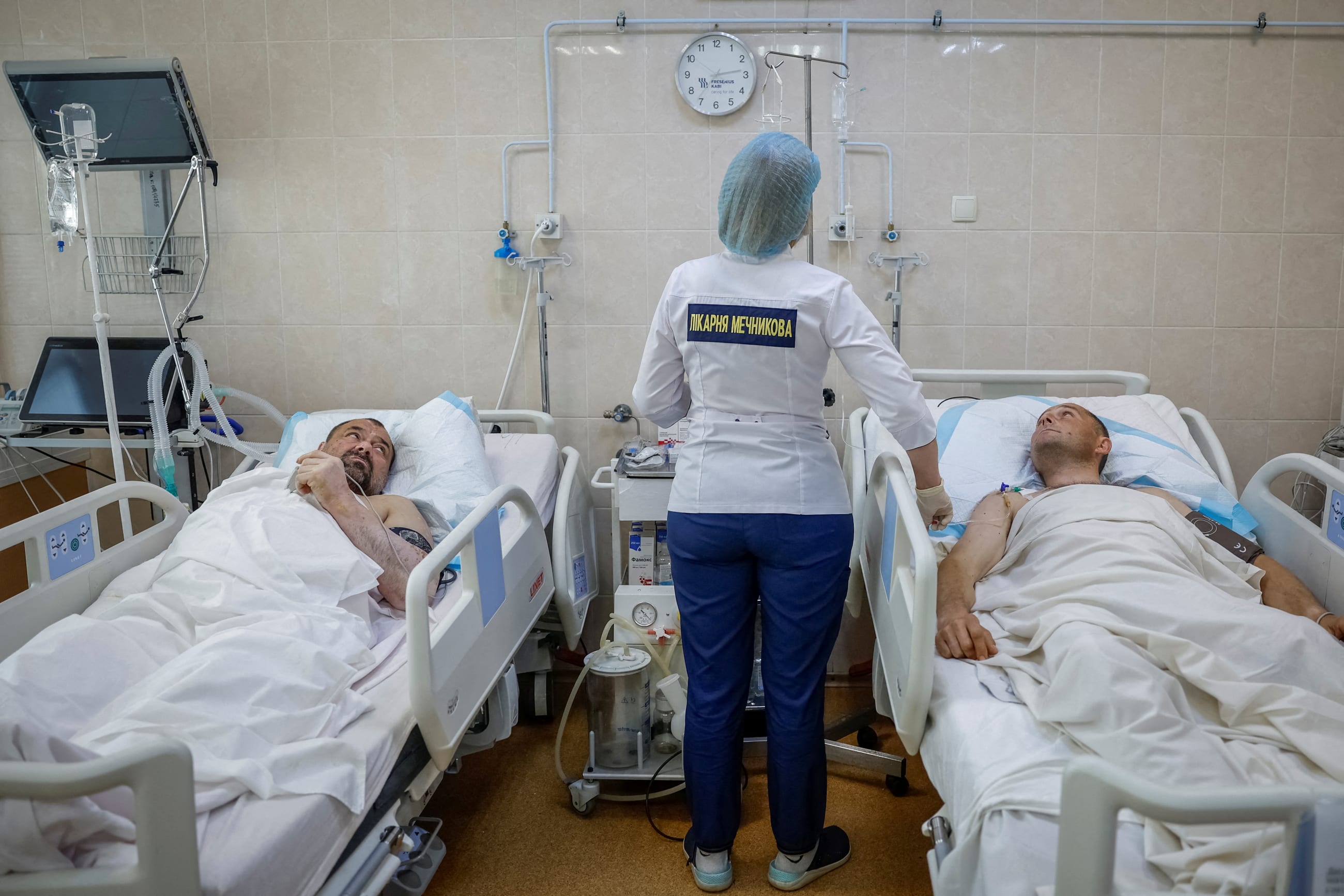
7. The War Wounded: A Doctor Reports 62 Miles From Ukraine's Front Lines
The signature wound of this war is limb amputation. Estimates reported in July stated that 30,000 to 100,000 Ukrainian soldiers and civilians have had a limb removed since 2022 and that a significant portion have lost more than one.
Most also suffer from concussions, traumatic brain injuries, posttraumatic stress disorder, or head and facial injuries. Those numbers could overwhelm any medical system. In comparison, the U.S. Department of Defense estimates that the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq resulted in a total of 1,705 amputees over a 16-year period.
8. A Reckoning for Attacks on Health in Gaza
During the course of the war in Gaza, as attacks on health care and denial of humanitarian aid became among its central features, Israel's posture on its legal obligations to protect health and health care devolved from feigned compliance and spurious reinterpretations of the law to open contempt for it.
9. Transparency Misinterpreted: CDC Vaccine Policy and Conflicts of Interest
A former Centers for Disease Control and Prevention director says the idea that the agency's vaccine advisors profited from their recommendations is a fallacy.
10. Vaccine-Preventable Disease: A Global Tracker
Think Global Health's disease tracker allows people from all regions to follow how these outbreaks develop, as vaccine access shifts worldwide.
11. Microplastics Above Mexico: A High-Altitude Search for Pollution
Alarming amounts of plastic are accumulating inside of human brains, roughly equivalent to the weight of a plastic spoon according to one study. A new study led by students at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) will shed light on the pattern of high-altitude snow and airborne microplastic pollution.
12. How the MAHA Commission Can Improve U.S. Life Expectancy
If the MAHA Commission really wants to increase life expectancy, it should work to provide consistent preventive care, including routine checkups, immunizations, lifestyle counseling, and medications.
13. Are Processed Meat, Sugary Drinks, and Trans Fats Safe at Any Level?
IHME's analysis estimates that a daily intake of 50 grams (1.8 ounces) of processed meat, equivalent to a standard hot dog, elevates the risk for type 2 diabetes by 30% and colorectal cancer by 26% relative to no consumption.
14. Colombia Opens South America's First Safe Injection Sites
Drug policy is contentious in Colombia, which produces the majority of the world's cocaine supply. The nation's overdoses increased by 356% between 2020 and 2021, from 8.5 incidents per 100,000 people to 40.5. This tragedy motivated the Colombian government to change its approach to overdose prevention and launch the 2023 National Drug Policy, which prioritizes health and well-being over criminalization.
15. Infrastructure, Cities, and Global Health Diplomacy
Built, social, and natural systems undergird human interactions in a globalized and ecologically interconnected world. In international society, countries use diplomacy to manage how different kinds of infrastructure connect and interact. In that sense, the built and social systems that support diplomacy are an infrastructure for global politics.
16. U.S. Deportees on Their Return to Guatemala
"I spent a lot of time hungry, cold and mistreated. This is the first decent meal I have received in several days."
17. Shifting the Narrative on Global Road Safety
A study examines the role journalism can play in preventing traffic collisions in five Anglophone African countries.
18. Visualizing Nutrition Deficits After USAID's Overhaul
Although increased investment in acute malnutrition treatment could achieve further reductions in child mortality, recent threats to funding for these programs could lead to a reversal in course. Even modest reductions in services could result in additional thousands of children's lives lost. In the face of such threats to services to address malnutrition, it is worth evaluating what is at stake.
Slashing Nutrition Treatment Could Lead to Excess Deaths
In Nigeria, funding cuts could lead to almost 19,000 additional child deaths from malnutrition

Baseline
Additional deaths with 49% reduction
The chart shows baseline and new excess deaths expected from malnutrition in Nigeria if funding is cut by 49% as projected by IHME's
computer simulation. Each child in the image represents approximately 483 deaths from malnutrition in Nigeria.
Chart:
Adapted from IHME by CFR/Allison Krugman • Source: IHME

Baseline
Additional deaths with 49% reduction
The chart shows baseline and new excess deaths
expected from malnutrition in Nigeria if funding is cut by
49% as projected by IHME's computer simulation. Each
child in the image represents approximately 483 deaths
from malnutrition in Nigeria.
Chart: Adapted from IHME by
CFR/Allison Krugman
Source: IHME
19. Intimate Partner Violence in Peru
Trainings, questionnaires, and other interventions are effective in preventing abuse only when victims trust institutions enough to disclose their abuse and have access to support.
20. From Long Flu to Long COVID: A Brief History of Postviral Illness
Chronic conditions stemming from infections, whether labeled influenza nervosa, myalgic encephalomyelitis, chronic fatigue syndrome, or long COVID, haunt individuals well after the initial illness subsides. Time and again, society has failed to reckon with these conditions, relegating their sufferers to the fringes of medical understanding and societal concern.
This trend is ancient. In 412 BCE, Hippocrates documented the Cough of Perinthus in a port city in northern Greece—the first known long flu, entailing "impaired night vision" and "paralysis of limbs."
21. Tobacco Control in Indonesia Hits Another Roadblock
"We are sad and disappointed. That the current finance minister openly visited tobacco factories seems to normalize the production and consumption of tobacco."
22. AI to Predict Suicide: The Case for Interpretable Machine Learning
With suicide rates rising, health systems overstretched, and trust in institutions fraying, people at risk need technologies that are both effective and ethically grounded. Interpretable machine learning creates an extraordinary opportunity to combine technological progress with empathy, allowing predictions to be made in ways that are understandable and fair.
23. U.S. Soft Power: Next Steps After the Foreign Aid Withdrawal
Given continued high levels of support for lifesaving programs by Americans across the political spectrum, one might wonder whether soft power still serves a purpose. Although transactional relationships could be useful in producing short-term narrow gains—similar to the threat of military action or withholding resources—soft power enables the United States to set the broader agenda in world politics.
24. Carterpuri: A Tribute to Jimmy Carter's Legacy in India
Recounting his impact on global health most likely won't be something you have already read. My tribute starts with a personal story about a small village in India halfway between my childhood home and my school. That's where I learned about President Jimmy Carter.
25. America First in Global Health: How Africa Should Respond
The first imperative is to reclaim the narrative. African governments should reject the framing of dependency as a moral failing and insist on recognizing the structural dynamics that created it. They need to articulate their vision of partnership: one in which external support strengthens rather than supplants national systems and accountability is mutual rather than one-sided.













